Laser cutting is a type of technology that has been around for quite some time, but it’s only recently that it has become more widely used in manufacturing and other industries. So, what exactly is laser cutting? How does it work? And what are its benefits? The brick engraving laser machines could also be used for laser cutting, expanding the range of materials and applications.
By the end, you should have a better grasp of the laser cutting concepts and how they can be used in various applications. Laser engraving for plastics is a precise and efficient method used to etch intricate designs, logos, or text onto various plastic materials, providing durable and high-quality results without compromising the integrity of the material.
What are the Five Applications of a Laser Cutter
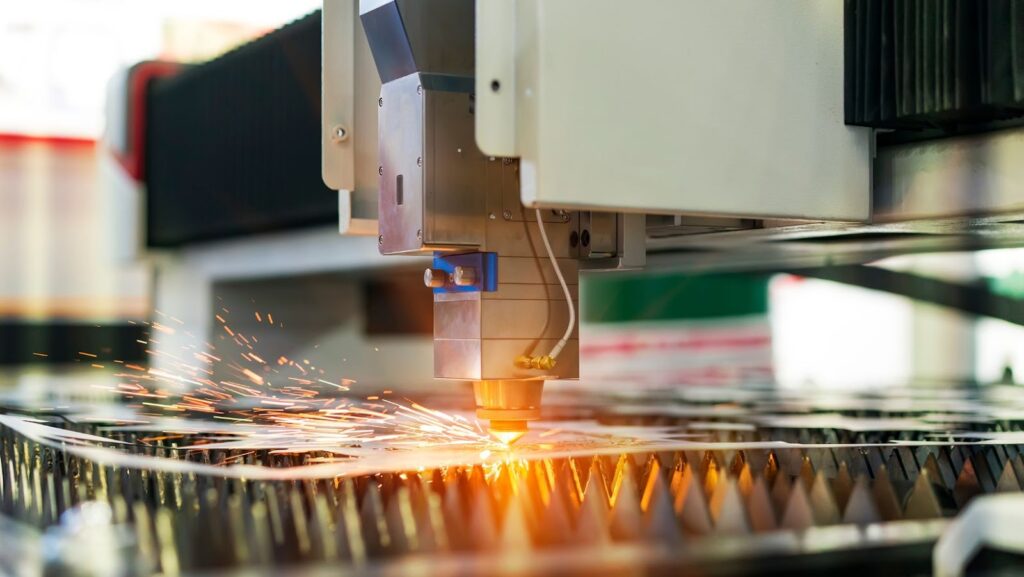
Laser cutting is a process that uses a focused laser beam to cut materials. The laser beam is generated by a laser, which is then directed at the material to be cut. The material is vaporized or burned by the laser beam, leaving a clean, precise cut.
Laser cutting has many applications in different industries. Some of the most common applications are:
1. Cutting metal: Laser cutting can be used to cut through metals of various thicknesses. The lasers used for this purpose are usually high-powered CO2 lasers.
2. Cutting wood: Laser cutting can also be used to cut through wood, although not as thick as metal. The lasers used for this purpose are usually lower-powered CO2 lasers or fiber lasers.
3. Engraving: Laser engraving is a process where the laser beam is used to etch a design or image onto the surface of the material. This can be done on both metals and wood. You can also laser cut acrylic materials.
4. Marking: Laser marking is similar to engraving, but instead of creating an image, it simply creates text or numbers on the surface of the material. This is often done for identification purposes, such as on parts or products in a factory setting.
5. Cutting fabric: Lasers can also be used to cut fabric, such as in garment manufacturing or upholstery production.

How does Laser Cutting Work Step by Step
Laser cutting is a process that uses a high-powered laser to cut materials like metal and plastic. The laser beam is generated by a laser source (usually a solid-state laser) and is directed at the material to be cut by a series of mirrors. When the beam hits the material, it vaporizes or melts it, making a clean cut. You have probably seen it in Bond movies; somehow, he always ends up tied with a laser beam slowly approaching and melting everything on its way.
Laser cutting is used in a variety of industries, including automotive manufacturing, aerospace, and electronics. It can be used to create intricate designs and shapes that would be difficult or impossible to create using traditional methods.
The first step in laser cutting is to create a computer file of the design that you want to cut. This file is then loaded into the laser cutter’s computer system. The cutter uses this file to direct the laser beam as it cuts through the material.
Next, the material to be cut is placed on the cutting table of the machine. The table can move in both X and Y directions so that the material can be positioned correctly for cutting. Most machines also have a Z axis, which controls the focus of the laser beam.
Once the material is in place, the machine’s operator will start the cutting process. The laser will start moving back and forth across the material, melting or vaporizing it as it goes. The speed and power of the laser can be adjusted depending on the thickness of the material and desired results.
Which Types of Lasers are most Common
Laser cutting is a fabrication process that uses a high-powered laser to cut materials like metal, plastic, and wood. The laser beam melts, vaporizes, or burns through the material, leaving a clean edge. Laser cutting is fast and accurate, making it ideal for prototyping and production runs.
There are three main types of laser cutting: CO2 lasers and fiber lasers. Each type of laser comes with its own set of advantages and disadvantages.
CO2 lasers are the most common type of laser used in manufacturing. They can cut through a variety of materials, including metals, plastics, and wood. CO2 lasers are fast and accurate, making them ideal for production runs. However, they require frequent maintenance and can be expensive to operate.
Fiber lasers are becoming more popular for industrial applications. They are more energy-efficient than CO2 lasers and can cut through thicker materials. Fiber lasers are also resistant to damage from dirt and debris. However, they have a smaller work area than CO2 lasers and cannot cut as many materials.
One honorable mention is excimer lasers and which are used in medicine for eye surgeries. They generate a high-energy UV light that can vaporize materials without touching them. Excimer lasers are very accurate but require special safety precautions because of the dangerous UV light they generate.